What are dual function transcription regulators?
Usually, the transcription regulators either repress or activate gene expression, however some rare quorum sensing systems have dual function transcription regulators. These are proteins that can either activate or repress gene expression depending on their binding state to DNA or, in some cases, autoinducer [reference]. For example, EsaR/I quorum sensing system has EsaR as its dual function transcription regulator and EsaI as its autoinducer synthase. EsaR can act as a repressor or an activator depending on presence of the autoinducer molecules known as acyl-homoserine lactones (AHL) [reference]. To further complicate things, the EsaR/I quorum sensing system has two promoters – PEsaR and PEsaS. EsaR can bind to both, if AHL is absent. However, while binding to PEsaR will lead to gene expression repression, binding to PEsaS will lead to activation. In turn, if AHL is present, an EsaR-AHL complex forms, which can no longer bind to either promoter. Thus, opposite effects will take place.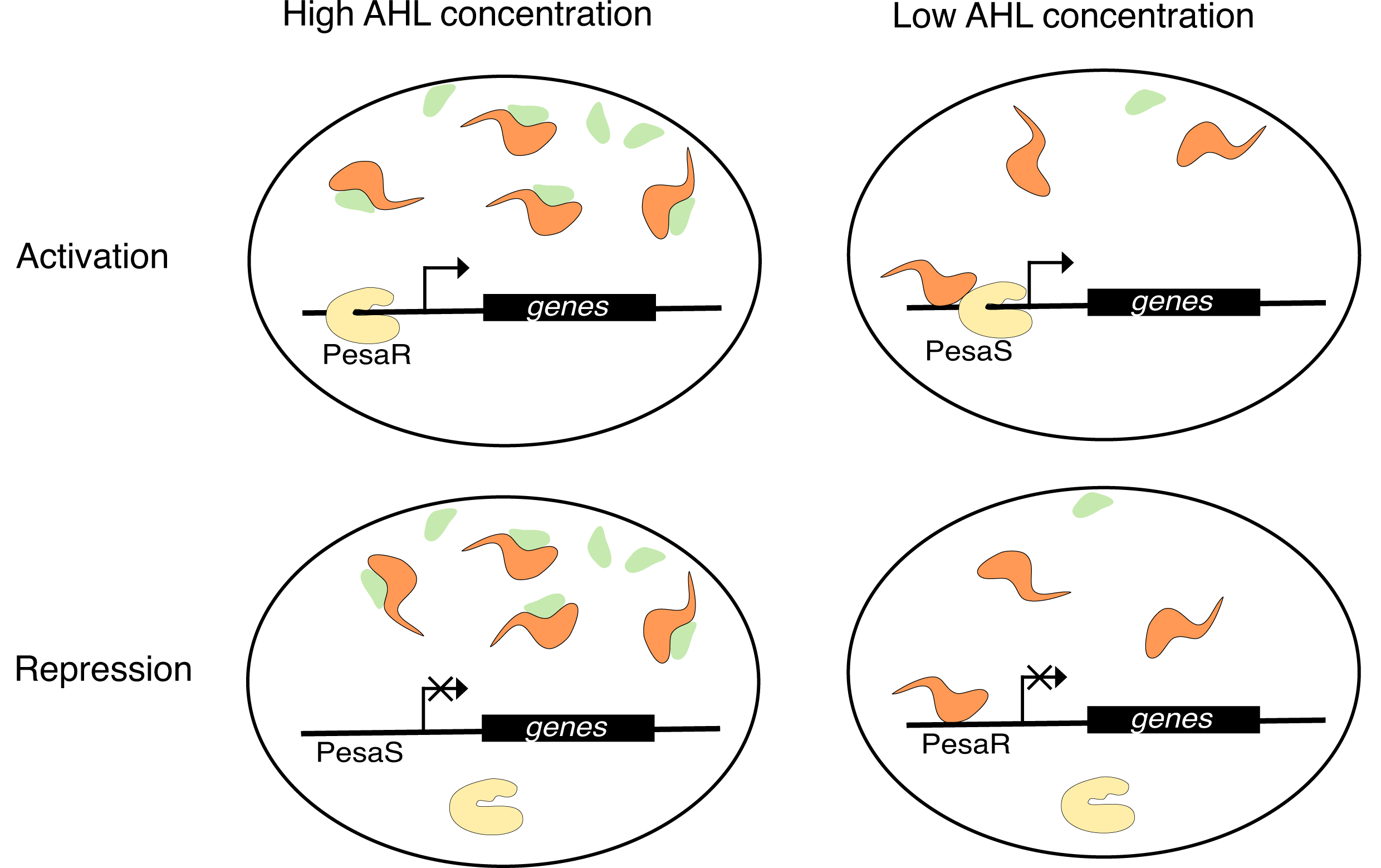
Why are they useful for Synthetic Biology?
Whole Cell Biosensors
Whole cell biosensors (WCB) are engineered cells that respond to external factors (e.g. light, chemicals) and express reporter genes in response. WCBs are a well-established area of synthetic biology, and WCBs have been successfully developed to detect arsenic pollution in the environment and clinically important biomarkers.Dual function transcription factors would allow increased complexity of biosensor circuits by allowing the expression of one reporter to be conversely coupled to the expression of another. This would allow the use of two different reporters for the biosensor to distinguish between molecules of interest, or for the biosensor to detect increases/decreases of the target molecule by expressing one reporter or the other. In the latter case, concentrations of the target molecule below a certain threshold could correspond to low levels of AHL and the expression of genes under PesaS, whilst concentrations above the threshold would correspond to high AHL and expression of genes under PesaR.
Metabolic Network Engineering
Metabolic engineering aims to increase yields of products from metabolic circuits by optimising the components in the metabolic pathway to minimise toxicity and burden. This allows expensive chemicals that are otherwise complex to synthesize to be produced by cells in a controllable manner, such as 1-butanol.The EsaR/I system was used by researchers in 2020 to create switches that could synchronise the up/down-regulation of genes used in a metabolic network, and used these switches to improve the production of 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) by 6- and 12-fold respectively. This can address two problems faced in metabolic engineering: dynamic regulation of essential genes and the reorientation of metabolic flux to production pathways.